1. Functional Additives
2. Fillers
3. Reinforcements
1. Anti oxidants
2. Heat stabilizers
3. UV stabilizers
4. Nucleating agents
Fillers:
1. Silicon dioxide - increase tear strength
2. Mica and talc improve stiffness, strength, hardness, heat distortion characteristics, dimensional stability and surface finish
3. Metal powders (aluminium, bronze, steel, lead, zinc, copper, nickel) improve heat distortion characteristics and particularly, electrical conductivity
4. MoS2 and graphite are used particularly in glass fiber reinforced polyamides to improve slip and wear characteristics.
Reinforcements:
- The main reinforcement for PA is glass fiber material.
- It is used in proportions of up to 50% w/w in PA 6 and PA 66 and upto 30% w/w in PA 69, 61, 11 and 12. Tensile strength, stiffness, hardness, heat distortion characteristics, tracking resistance, chemical and hydrolysis resistance are all improved.
- Carbon fibers increase the elastic modulus significantly more than glass fiber material and also improve slip properties, thermal and electrical conductivity
Grades of Polyamide 66
The Polyamide 6 is available in various grades
- Injection molding grade
- Extrusion grade
- Rotational Molding grade
- Fluidized bed coating grade
Processing considerations for Polyamide 66
- The Polyamide 66 is also processed with much precautions as like Polyamide 6.
- The annealing temperature of Polyamide 66 part is 149 – 177°C.
- The Polyamide 66 is processed in the temperature range of 260-320°C.
- The material has to be predried at 80°C for 2 - 4 hours
- Injection moulding, Extrusion techniques, Compression moulding, Foam moulding and Rotomoulding techniques are used for processing the materials.
- While moulding Polyamide 66, the precautions what are taken for Polyamides 6 the some should be taken for Polyamide 66.
Surface finishing of Polyamide 66
- Moldings may be painted or printed without pretreatment
- The high resistance of PA to solvent facilitates coating and even recoating with stoving requires bond on UF or MF resins
- Mouldings can be colored by immersing in aqueous or alcoholic solution of dye stuffs, particularly azo dyes
- Hot embossing with suitable foils pose no problem
- Metal finishes are applied by vacuum metallization
- In Recent years there has been growing interest in electroplated PA moldings
- These require extremely high quality surfaces
- Products containing fillers are used for reflective electroplated parts
- Special purpose glass fibre reinforced grades are suitable for moldings with extruded surfaces
- Applications include wheel trims, door handles, window winder and water fittings
Machineability of Polyamide 66
Cutting
- Casted products/ molded products are workable with most of the tools and machining which are designed for working with wood and metal.
However higher efficiency is obtainable with equipment specially designed for plastics.
Joining
- PA components are frequently joined with ordinary or self-lapping screws and rivets as well as snap connectors.
Welding of Polyamide 66
- All processes developed for welding thermoplastics are suitable for polyamides.
- The preferred methods are ultrasonic friction and heated tool welding (heating by contact or radiation).
- High frequency and heat impulse welding are used mainly for joining films.
- The ultrasonic method enables welding of standard injection molded parts to be integrated in automated production.
Bonding of Polyamide 66
- Polyamides can be bounded with numerous adhesives based on solvents or lacquers.
- An adhesive can be quickly prepared by shaking a rerorcinol/ Ethanol solvent mixture for 15 minutes.
- Concentrated formic acid, dimethyl formamide and aqueous phenol (12% water) are also suitable.
- A polyamide containing calcium carbide/ ethonal solvent adhesive can be used for food applications or in water supplies.
- It is resistant, non-toxic and odour-free, solid adhesives with or without chemical cross linking can be used for example for bonding bearing bushes into metal assemblies.
Applications of Polyamide 66
Areas of applications are very similar to Polyamide 6.
- Appliances - Automotive
- Business equipment. - Hardware
- Consumer Products. - Electrical
- Machinery and packaging
Hammer handles of glass reinforced Polyamide are superior to wood they replaced (Application related to hardware)
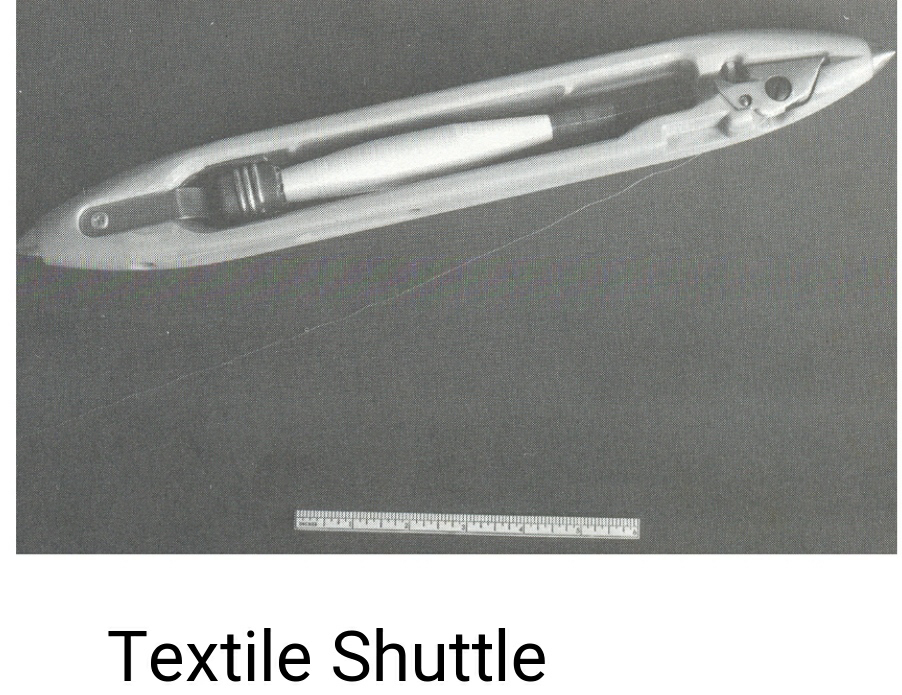
Textile shuttle of glass reinforced Polyamide 66 with stand frictional heat and millions of impacts (Application related to machinery)Gide shoes for the hand rail of moving stairway are made of Polyamide 66 with molybdemum disulfide added for lubricity (Machinery) Polyamide elevators gibs slide thousand of miles against steel rails with minimum lubrication (Example of good abrasion resistance, application of machinery) Trimming sprocket for automobile cam shaft has Polyamide 66 teeth for long wear and noise reduction (Automotive) Countless electrical coils are wound on Polyamide 66 (Electrical) Spatula blades and spoons of Polyamide 66 (consumer products, kitchen)Applications as gears, bearings in Pump parts
In Automotive Applications
In Automotive Applications
Blends of Polyamide 66/PE
- In compatible hydrocarbon polymers such as PE can be melt with Polyamides to yield compositions that have improved higher permeability and are processable film and filaments and bottles.
- Improvement in moisture absorption, impact strength, flexibility, moulding characteristics and structure uniformity are claimed for blends made from Polyamide and ethylene / alkyl acrylate ester copolymers
Blends of Polyamide 66/PPO
The alloys of polyamide (Polyamide 66, and PPO) are used as a commercial products because higher HDT and reduce sensitivity to moisture. Toughness are use to reduce brittleness of these blends.
List of Manufacturers /Suppliers of Polyamide 66










No comments:
Post a Comment