HIPS is manufactured by dissolving unsaturated rubber in styrene monomer and polymerizing the monomer in a solution or mass-suspension process.
The rubber is generally polybutadiene.
- In this process the resultant blend will contain not only rubber and polystyrene but also a graft polymer where short styrene side chains have been attached to the rubber molecules and this enhances the impact strength.
- The rubber content in solution polymerization can go up to 14% by weight.
- HIPS obtained by this process are having impact strength 7 times greater than GPPS.
Crystal polystyrene can be processed by every conventional technique used for thermoplastics. Drying is normally not necessary. But if necessary (high transparency and high gloss required), the product can be dried for 2 hours at about 80°C..
Injection moulding:
A melt temperature of 180-280°C is recommended. Generally, mold temperature should lie between 30 and 50°C. For thin wall objects moulded at short cycle times it could be useful to cool down the mould down to 10°C.
Mold shrinkage lies between 0.4 and 0.7% depending on the grade used.
Extrusion moulding:
Grades with a high viscosity are suitable for extrusion.
A melt temperature of 180-220°C is generally used.
Processing of HIPS
- Thermoforming
- HIPS is one of the major thermoforming materials. Solid sheet of HIPS is extruded and shaped by a variety of forming methods.
- The most common method is in-line vacuum forming.
- In this process, vacuum is drawn between sheet and mold or pressure is applied to the mold plug while air is drawn out from the space the sheet and mold.
- Typical forming temperature range is around 130° to 180°C and temperature at which forming may be removed from the mould is at 85°C.
APPLICATIONS OF HIPS
Electrical/Electronics
Computer housing, radio TV and transistor cabinet, refrigerator grills, knobs and linings, air-conditioner and air-cooler front grills, telecommunication and power cable joints.
Households
Coffee sets, jars, dishes, egg trays, gift articles, knife handles, bath tubs, disposable cups, toilet seats, safety razors, pen barrels, toys
Packaging
Vacuum formed trays and bowls for packaging of food
Industrial
Strengths:
1. Tougher than PS crystal
2. Low cost
3. Good dimensional stability
4. Good processability
5. Good electrical properties, low dielectric loss
6. Excellent resistance to gamma radiation
7. FDA compliant
Limitations:
1. Reduced transparency compared to PS crsytal
2. Reduced electrical properties compared to PS crystal
3. Poor chemical resistance, especially to
organic solvents
4. Susceptible to UV degradation
5. Highly flammable and toxic smoke
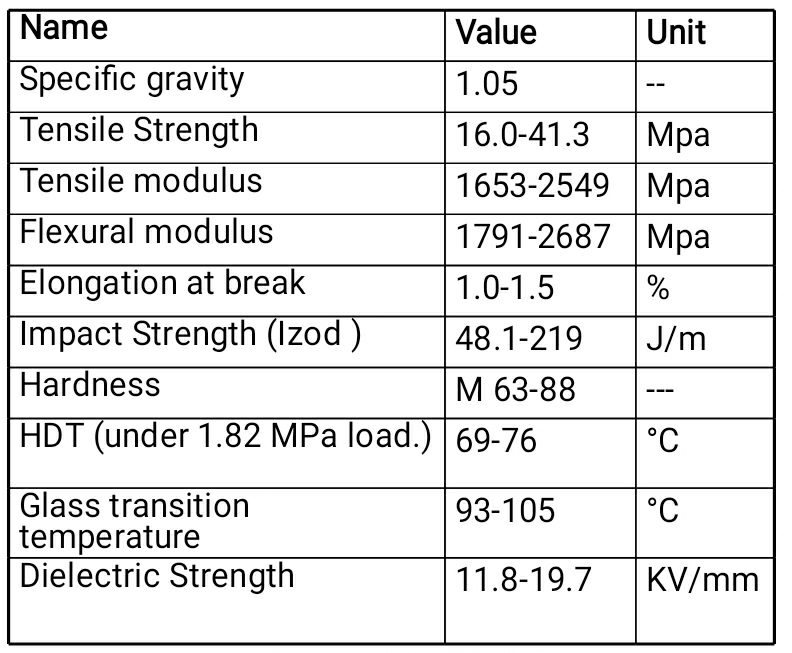
General Properties
- Good dimensional stability even at low temperature and high impact strength than the general purpose polystyrene.
- Good toughness, ease of processing, higher resistance to stress cracking.
- High elongation at break, less resistance to ageing than GPPS.
Properties
1. Resistant to mineral acids, caustic liquids and water
2. Good dimensional stability even at lower temperature
3. High impact strength compared to GPPS (7 times than GPPS)
4. Heat stable compared to GPPS
5. Higher resistance to stress cracking than GPPS
6. High elongation at break
7. Dissolved by alcohols, esters, ketones, ethers and oils
8. Radiation resistance is significantly lower than GPPS.




No comments:
Post a Comment